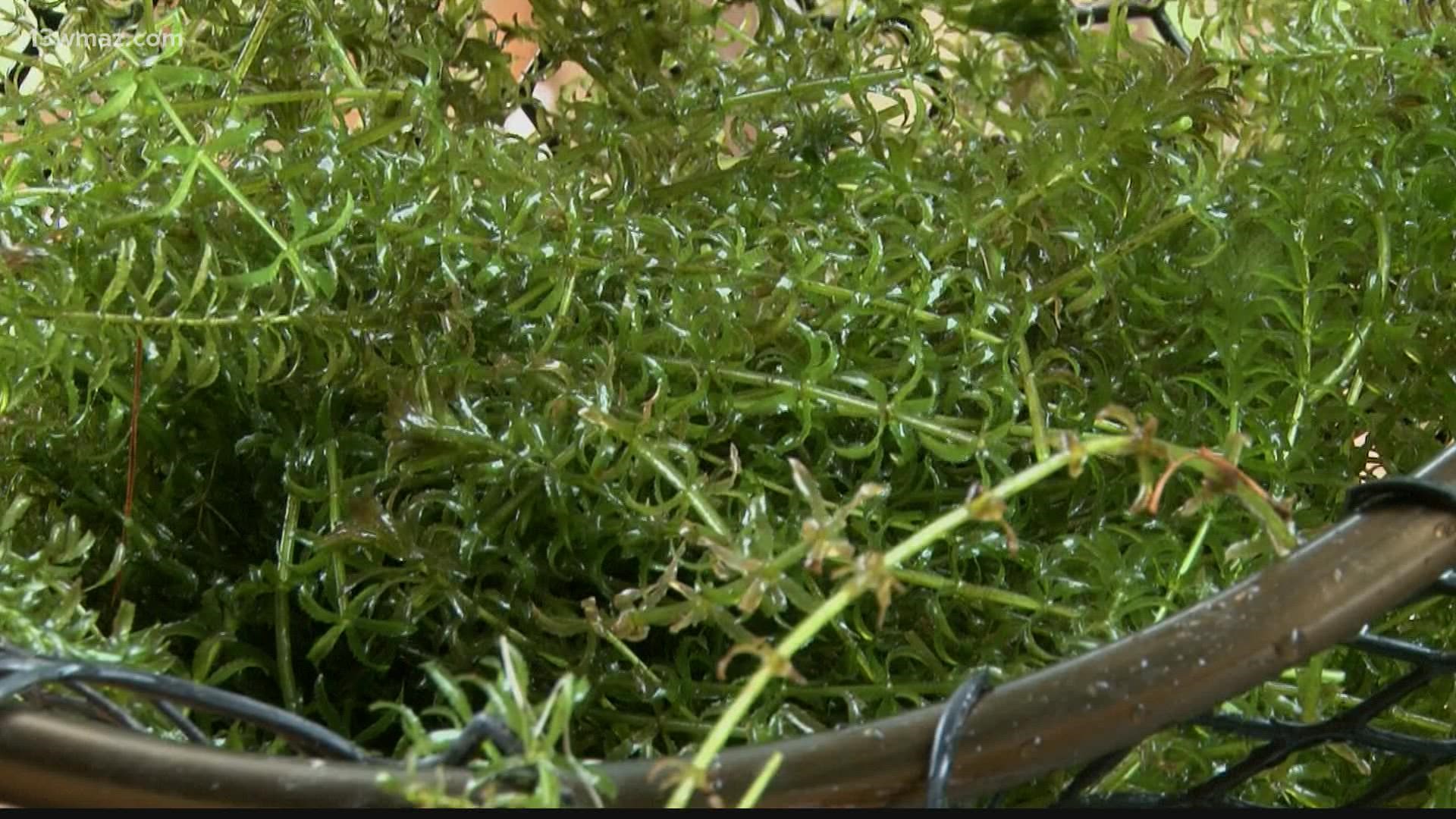
Hydrilla, also known as water thyme, is an invasive aquatic plant that can quickly overtake bodies of water, choking out native vegetation and disrupting ecosystems. Managing and controlling hydrilla infestations is crucial to maintaining the health and balance of aquatic environments. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore proven methods for getting rid of hydrilla and restoring the natural balance of your waterways.
Understanding Hydrilla
Before delving into eradication methods, it’s essential to understand the characteristics and behavior of hydrilla. Hydrilla is a submerged aquatic plant with long, slender stems and small, serrated leaves arranged in whorls. It can grow rapidly under favorable conditions, forming dense mats that impede water flow, inhibit oxygen exchange, and disrupt aquatic habitats.
Asessing the Infestation
The first step in combating hydrilla is to assess the extent of the infestation. Conduct a thorough survey of the affected water body to determine the size and density of the hydrilla population. Identify areas of dense growth and potential entry points for new infestations. This information will guide your eradication efforts and help you develop an effective management plan.
Mechanical Control Methods
Mechanical control methods involve physically removing hydrilla from the water. This can be done using various techniques, including:
Hand Pulling
Small-scale infestations can be manually removed by hand. Wear protective gloves and use a rake or aquatic weed puller to grasp and pull out hydrilla plants from the water.
Cutting and Harvesting
Use cutting tools such as aquatic weed cutters or aquatic herbicidal cutters to trim and harvest hydrilla plants. Regular cutting can help reduce the spread of hydrilla and prevent it from forming dense mats.
Barrier Installation
Installing physical barriers such as bottom barriers or floating curtains can help contain and restrict the spread of hydrilla in larger water bodies. These barriers prevent hydrilla fragments from dispersing and establishing new colonies.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control methods utilize natural predators or pathogens to target and suppress hydrilla populations. Common biological control methods include:
Biological Control Agents
Introduce biological control agents such as grass carp or certain insect species that feed on hydrilla. These agents can help reduce hydrilla biomass and limit its spread in aquatic environments.
Herbivorous Fish
Stocking herbivorous fish species such as tilapia or koi can provide ongoing control of hydrilla by grazing on the plants and preventing excessive growth.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control methods involve the use of herbicides to target and kill hydrilla. Before using herbicides, it’s essential to consult local regulations and obtain necessary permits. Common herbicides used for hydrilla control include:
Fluridone
Fluridone-based herbicides are effective in controlling hydrilla by inhibiting photosynthesis. Apply fluridone treatments according to label instructions and monitor water quality during and after treatment.
Diquat
Diquat-based herbicides are contact herbicides that kill hydrilla on contact. Use diquat treatments selectively to target hydrilla while minimizing harm to non-target vegetation and aquatic life.
Implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM) Strategies
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) involves combining multiple control methods to achieve long-term, sustainable hydrilla management. By integrating mechanical, biological, and chemical control methods, you can effectively reduce hydrilla populations and minimize the risk of resistance or environmental harm.
Conclusion
Getting rid of hydrilla requires a multifaceted approach that combines mechanical, biological, and chemical control methods. By understanding hydrilla’s characteristics, assessing the infestation, and implementing appropriate control measures, you can effectively manage hydrilla populations and restore the health and balance of aquatic ecosystems. Follow these methods to combat hydrilla and preserve the beauty and biodiversity of your waterways.